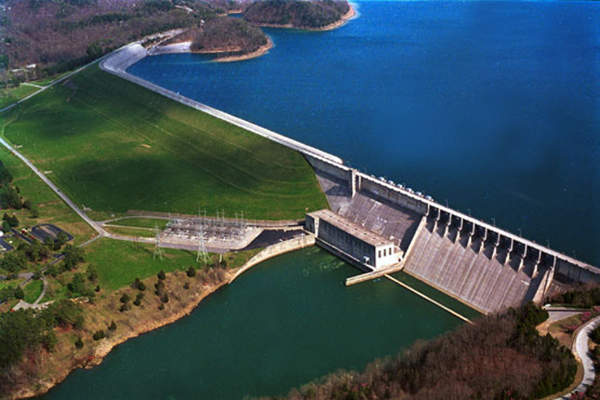
The US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) completed foundation remediation works for the Wolf Creek Dam in March 2013. The completion ceremony for the project was held in April 2013. Wolf Creek is a multipurpose dam which provides hydropower, flood control, navigation, water supply and recreation.
The project was carried out to prevent possible flooding from the dam, which experienced seepage issues for more than five decades. Property damage worth $3bn is estimated on occurrence of a potential breaking of the dam.
The construction works for the Wolf Creek Dam’s foundation remediation commenced in 2008 with the construction contract awarded to the joint venture of Treviicos and Soletanche. The project value was about $594m, which mostly comprised of federal funding.
History of Kentucky’s Wolf Creek Dam
Construction of Wolf Creek Dam commenced in 1941 following authorisation provided by the Flood Control Act of 1938, and was completed in 1951.
The dam was built on the Cumberland River located in south central Kentucky. The geology of the location is mainly composed of Karst formations, which lead to the breakup of the limestone in the dam’s foundation. The dam first witnessed seepage in 1968.
First efforts to avoid seepage were made from 1968 to 1970 by grouting the dam’s foundation. A major construction project was carried out from 1975 to 1979, in which a reinforced concrete cut-off wall was constructed through the earth embankment into the rock foundation. The problem was still not solved, with seepage intensifying in 2005.
The remediation project work was the second phase of the major dam reinforcement project. The first phase comprised of the initial remedial works commencing in 2006 and the grouting of the foundation commencing in 2007.
Dam and power station details
Wolf Creek Dam is a concrete-gravity and earth-fill dam, measuring 79m in height and 1,748m in length. The dam has a volume of 8.7 million m³ and impounds the Cumberland River.
The dam creates the Lake Cumberland reservoir, with a capacity of 7.5 million m³. The catchment area of the reservoir measures 14,990km² and the reservoir covers a surface area of 20,340ha, with a flood storage reservoir capacity of 2.09 million acre-feet.
The dam’s power station comprises of six turbines with an installed capacity of 270MW. The spillway of the dam comprises of ten radial crest gates and six sluice gates.
Foundation remediation project details
The project comprised of constructing a new barrier wall upstream on the right side of the concrete monoliths, to stop seepage in the Karst geology of the rock. A protective concrete embankment wall (PCEW) was also constructed to protect the embankment during the construction of the main barrier wall.
The construction of the main barrier was completed in March 2013, ahead of the estimated December 2013 schedule. The barrier wall utilised about 1,197 piles measuring three feet in diameter and extending up to 275ft deep into the bedrock below the foundation of the embankment, which is about 75ft deeper than the original wall. The barrier wall measures 4,200ft in length, which is about 61% longer than the existing wall.
The protective embankment wall constructed of concrete is six foot wide and about 230ft deep. The extension of the wall along the embankment is about 3,600ft. The construction of the protective wall was completed in June 2012.
Up to 13 drilling rigs were used at the construction site for the creation of the main barrier wall, where constructors operated in a cramped work space measuring 80ft in width and 4,000ft in length. USACE now plans to maintain the lake at elevations of 700ft to 705ft, which is about 20ft higher than the current range 680ft and 685ft.
Contractors involved with USACE’s Wolf Creek Dam project
The concept study for the project was carried out by Black & Veatch. The AquaTrack survey to study the groundwater system at the dam was conducted by Willowstick, in collaboration with Arcadis. Wassaras provided its water-powered drilling equipment for drilling the bore holes and the pilot holes.
Related content
San Vicente Dam Raise, San Diego, California, United States of America
The San Diego County Water Authority (SDCWA) is undertaking a $530m project to raise the San Vicente Dam in San Diego, California, US.
Grand Coulee Dam, Columbia River, Washington, United States of America
Grand Coulee is a gravity dam on the Columbia River in the US, which serves the purposes of irrigation, flood control and power generation. It forms part of the US Bureau of Reclamation’s Columbia Basin Project which irrigates the central Washington state area.