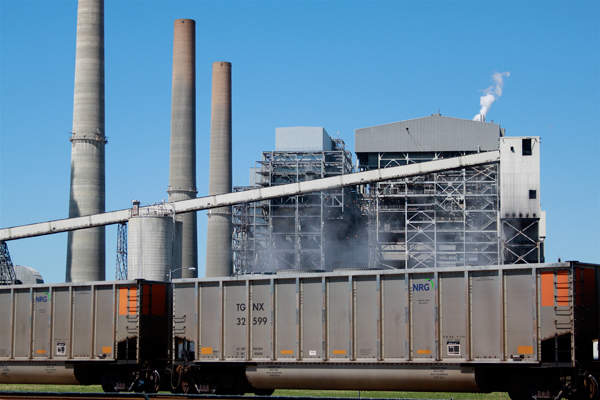
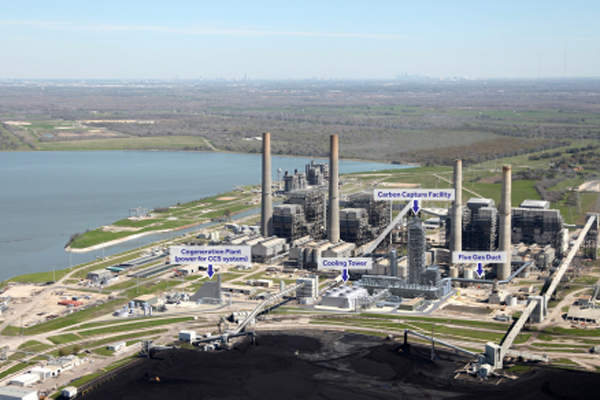
A commercial scale post-combustion carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) project is being developed at NRG Energy’s WA Parish coal-fired Generating Station, one of the ten biggest power stations in the US. The plant is located in Thompsons, Fort Bend County, about 60km south-west of Houston, Texas.
The WA Parish CCS project, also known as the Petra Nova Carbon Capture Project, will capture approximately 90% of the carbon dioxide (CO2) from a 240MW slipstream of flue gas from the power station’s existing 610MW coal-fired Unit 8, and extract approximately 1.6 million tons (mt) of CO2 each year. The CO2 will be used for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) at the West Ranch Oil Field located on the Gulf Coast of Texas.
The CCS project, estimated to cost $1bn, will be built and operated by Petra Nova CCS I, a joint venture between Petra Nova Holdings, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG Energy, and JX Nippon Oil Exploration (EOR), a wholly-owned subsidiary of JX Nippon.
The project is scheduled for completion by the end of 2016 and is expected to be the world’s biggest post-combustion carbon capture facility on an existing coal plant.
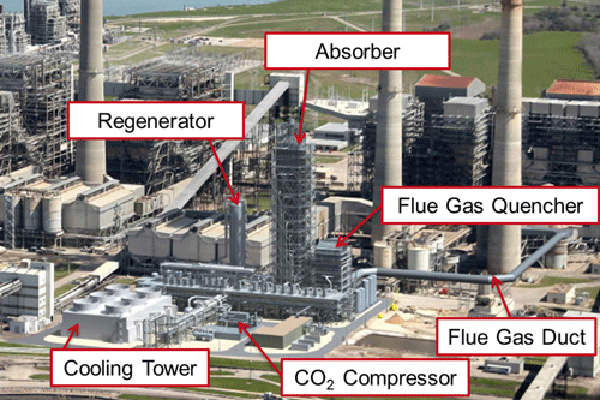
Carbon capture process at WA Parish power station
The existing coal-fired unit of the WA Parish power station that will host the CCS project already has a system in place for treating flue gas for the reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and sulphur dioxide (SO2). The treated portion of the flue gas will be diverted to the new CCS system.
The flue gas first passes through the flue gas cooler where it is cooled, dehydrated and stripped of its remaining SO2 content. Next, the cooled flue gas comes into contact with a circulating sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution.
Related content
White Rose Carbon Capture and Storage Plant, North Yorkshire, UK
The proposed White Rose Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) power project near the Drax power atation site, Selby, North Yorkshire, UK, will be the world’s biggest CCS power plant using oxyfuel combustion technology.
The cooled and conditioned flue gas is then directed to the CO2 absorber where the amine-based solvent captures CO2 through a chemical reaction. The carbon-free clean flue gas is released into the atmosphere. The CO2 containing solvent then enters the regenerator or stripper where it is separated from the solvent using low-pressure steam, with the heat of the steam breaking the weak bond between the CO2 and the solvent. The captured CO2 is then compressed and dried before being sent to a pipeline. The CO2-stripped solvent is sent back for further carbon capture.
The project’s carbon capture capacity is expected to be 4,776t per day. A cogeneration plant comprised of a combustion turbine and a heat recovery boiler at the host unit of the power station will provide power and thermal energy required for the CO2 capture and compression system’s operation.
Transport and the use of captured carbon
The captured CO2 will be transported via an 85-mile pipeline connecting the West Ranch Oil Field, located near Vanderbilt, Texas, to a reservoir for enhanced oil recovery (EOR). The oil field, which has been in production since 1938, is owned by the NRG-JX Nippon joint venture (50%) and Hilcorp Energy (50%).
EOR will be able to recover an estimated 60 billion barrels of oil from the field. The Petra Nova CCS project is expected to boost the field’s production from 500 barrels per day (bpd) to 15,000 bpd.
Carbon capture technology at the Petra Nova project
The Petra Nova CCS project uses a CO2 recovery technology called the KM-CDR Process, which was jointly developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and the Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO). The technology uses a proprietary amine solvent called KS-1, which is specially formulated for low cost and low energy-consuming CO2 absorption and desorption.
Financing for the CCS project
The US Department of Energy (DOE) is providing a grant of up to $167m for the WA Parish Carbon Capture project, the first commercial-scale post-combustion CCS project in the country, as part of its Clean Coal Power Initiative Program (CCPI), a cost-sharing collaborative programme between the federal government and private industry.
The Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) and Mizuho Bank, backed by Nippon Export and Investment Insurance (NEXI), are providing loans worth $250m for the project.
The JV partners NRG and JX Nippon are contributing $300m each as equity investment for the project.
Contractors involved with Petra Nova Carbon Capture project
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and The Industrial Company (TIC) were awarded the engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contract for the CO2 capture system and ancillary facilities of the Petro Nova CCS project in July 2014.
MHI will license carbon capture technology to Petra Nova CCS I through its wholly-owned subsidiary Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America (MHIA).