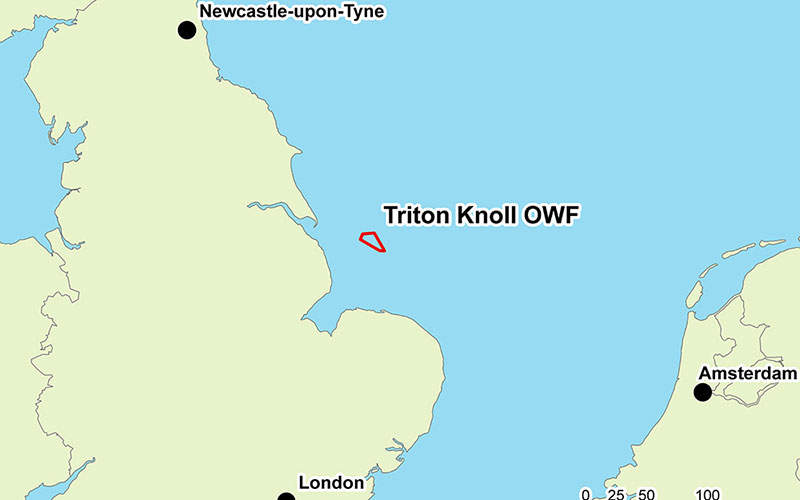
Triton Knoll is a Round 2 offshore windfarm in the UK, being developed by innogy, a subsidiary of RWE. It is located within Greater Wash Strategic Area, 33km away from the coast of Lincolnshire in the North Sea. The windfarm will have an installed capacity of 860MW.
Estimated to cost £2bn, the project achieved financial closure in August 2018. innogy also signed an agreement to sell a 41% stake in the project to J-Power (25%) and Kansai Electric Power (16%) in August 2018. innogy currently owns a 59% stake in the Triton Knoll project.
A group of international banks is financing the Triton Knoll offshore windfarm. The consortium comprises KfW IPEX-Bank, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking, MUFG Bank, ABN AMRO Bank, ING Bank, and Lloyds Bank.
The offshore windfarm will create approximately 3,000 jobs during the construction phase and 325 jobs during operation.
When operational in 2021, it will generate an annual electricity equivalent to the domestic needs of up to 800,000 average UK households. It is expected to offset more than 12.88 million tonnes of CO2 and 29,929t of SO2 a year.
Project background
The Crown Estate and the government opened the second tender round for offshore windfarm development sites within three selected strategic areas around the coast of the UK in 2003. The Knoll offshore windfarm development licence was awarded to RWE under the Round 2 tender process.
Offshore and onshore environmental surveys at the offshore windfarm location were completed in 2008 and 2009 respectively. The consultation on onshore substation options was completed in 2010 and formal consultation on the offshore components of the project was concluded in 2011.
The project planning application submitted to the Infrastructure Planning Commission was accepted for examination in 2012.
Triton Knoll received a development consent order (DCO) for the offshore array component from the UK Secretary of State for Energy and Climate Change in July 2013. The overall capacity of the project was reduced from the original 1,200MW to 900MW in 2014.
RWE Innogy and Statkraft signed a 50:50 partnership agreement to jointly develop the windfarm in February 2015. Statkraft’s 50% stake in the project was acquired by Innogy in October 2017.
The DCO application for electrical system components of the offshore windfarm was submitted in 2015. The electrical system planning application was accepted in September 2016. The project received a Contract for Difference (CFD) from the government in September 2017.
Triton Knoll wind farm make-up
The project is being developed in two separate packages, including offshore array and electrical system components.
The offshore array will constitute wind turbines, meteorological masts, offshore substations and the cables that link the wind turbines to the offshore substations. The electrical system will include the substation, underground cables, offshore export cables and electrical compound along the onshore cable route.
Triton Knoll offshore windfarm will be installed with up to 288 wind turbines with a capacity between 3.6MW and 8MW. The foundations will be laid at a water depth of 18m.
The maximum height of the turbine will be 220m to the tip of the blade, the hub height will be 140m, and the rotor diameter will be 180m. The windfarm will include up to five meteorological masts for wind data collection.
Generation and transmission of electricity from Triton Knoll windfarm
The windfarm will be connected by four export cables and six onshore cables. The turbines will be connected to the offshore substation by means of buried intra-array cables, while a 37-mile onshore cable will be laid from Anderby Creek to Bicker Fen. A mobile facility will be set up for the operations and maintenance staff and equipment.
The windfarm will be connected to Triton Knoll substation 1 and substation 2 transformers through an intermediary electrical compound located in the East Lindsey District Council area near Bicker Fen south-west of Boston, Lincolnshire.
Power purchase agreement
Ørsted signed a power purchase agreement (PPA) with innogy in August 2018, to offtake 100% of the power generated by the wind for a term of 15 years.
Construction of Triton Knoll windfarm
The onshore construction began in September 2018, while the offshore construction will commence near Orby, Lincolnshire, in 2019.
Contractors involved
Shoreline was contracted for simulation studies of the O&M marine logistic strategies at the offshore windfarm in December 2015. The scope of the study includes build-up of virtual windfarm layouts, and subsequent simulation and consideration of various marine logistic and manning concepts, including CTV, SOV, SES, HLV and helicopters, using MAINTSYS, which is a computer-based simulation software developed by Shoreline.
MPI Offshore was contracted to install 92 foundations and two substations in October 2017.
Siemens Transmission and Distribution was awarded the contract to provide engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) services for the onshore and offshore substations in October 2017.
MHI Vestas was contracted for supplying 90 V164-9.5MW turbines for the Triton Knoll offshore windfarm.
NKT, in a consortium with Boskalis Subsea Cables and Flexibles (VBMS), is responsible for supplying the export and array cable systems for the project. Murphy Group handles the design and cable work of the windfarm.
Nexans was contracted by J Murphy and Sons for the supply of cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated alternating current (AC) cables.
Under a two-year agreement with Murphy Group, Scarborough Nixon Associates and TM Links were selected to provide ecologists and traffic management for the project.
A consortium of Smulders and ENGIE Fabricom was awarded a contract by Siemens Transmission & Distribution for building two Offshore Transformer Modules (OTMs) for the Triton Knoll offshore windfarm.
JGC Engineering and Technical Services was sub-contracted by Siemens Transmission and Distribution for supplying high-voltage equipment containers fabrication and fit out for the project.
Seaway Heavy Lifting, a subsidiary of Subsea 7 Renewables & Heavy Lifting Business Unit, was contracted for transporting and installing the 90 WTG foundations, along with two offshore substations for the windfarm.
GeoSea, a subsidiary of DEME, is responsible for transporting and installing 90 wind turbine generators at the project site.
Offshore Wind Consultants was contracted to provide project management services to the Triton Knoll offshore windfarm.