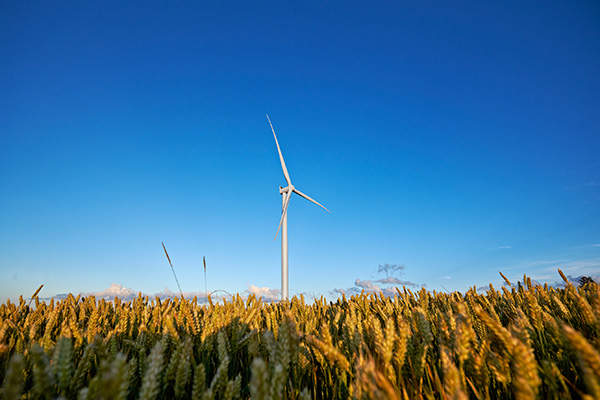
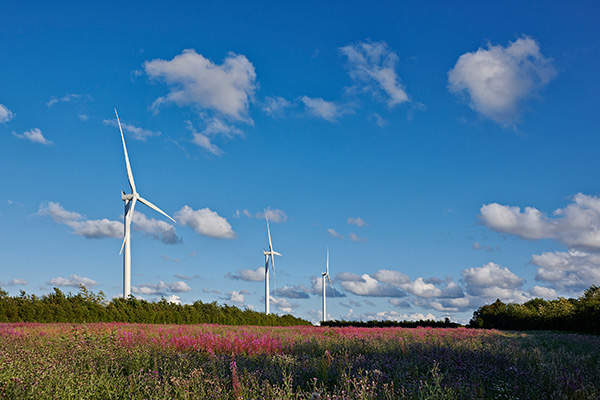
Pen y Cymoedd is an onshore windfarm built in the county boroughs of Neath Port Talbot and Rhondda Cynon Taf, South Wales, UK. With an installed capacity of 228MW, it is the biggest onshore windfarm in England and Wales.
The £400m ($635m) windpower project was developed by Swedish company Vattenfall. The facility has an operational life of 25 years and generates enough electricity to power 1,88,000 homes a year.
Construction of the project began in February 2014 and was completed in the second quarter of 2017. The construction phase employed more than 1,000 workers The windfarm was officially inaugurated on 28 September 2017.
Plant details and grid connection
The windfarm was developed on publicly owned land managed by Forestry Commission Wales in the Upper Afan Valley in South Wales. It has 76 Siemens SWT 3.0 direct drive wind turbines rated 3MW each.
The transmission infrastructure for the windfarm includes two new substations connected by 9.2km of underground cables. The electricity produced by the hillside turbines is stepped up from 33kV to 132kV by the Pen y Cymoedd substation. The second substation at Rhigos further steps up the voltage to 400kV for input into the new National Grid substation through overhead lines.
A compact plug and switch system (PASS) hybrid switchgear rated at 132kV was installed at the hillside Pen Y Cymoedd substation for sub-transmission. The substation is also equipped with voltage source, converter-based, reactive power compensation units, called PCS 6000 STATCOM, in order to support the stability of grid voltage using variable reactive power during voltage fluctuations.
Both the substations were supplied with automated equipment that is compliant with the IEC 61850 international standard of communication in substations for effective protection, control and monitoring of the flow of electricity.
Pen y Cymoedd wind farm construction
The first phase of construction involved civil and electrical works, including construction of the site welfare compound, site access tracks, crane pads, underground electricity cables, turbine foundations and an onsite control building. The second phase of construction included turbine installation and additional civil works.
More than 6,000t of steel reinforcement and 50,000m³ of concrete was to build the windfarm’s turbine bases. The site also required the construction of 80km of cabling and 80km of access tracks. The final turbine was installed in May 2017.
To lay the turbine foundation, holes measuring 4.5m in depth and 30m in diameter were excavated. Steel reinforcement was performed onsite and fixed in the excavation before concrete was poured continuously for 12 hours to form the turbine foundations. Up to nine steel fixers and eight concrete workers were required to pour the concrete for each base.
Twenty five 3.6MW wind turbines have been installed at the 90MW Burbo Offshore Wind Farm in Liverpool Bay, Wales.
The underground cables pass through a high-pressure gas pipeline and are located close to an ancient monument and an area of scientific importance, so a singular trenching technique was used to minimise disruption.
Contractors involved with the project
A 50:50 joint venture between Jones Bros and Balfour Beatty was awarded a contract to provide civil and electrical infrastructure for the windfarm in October 2013.
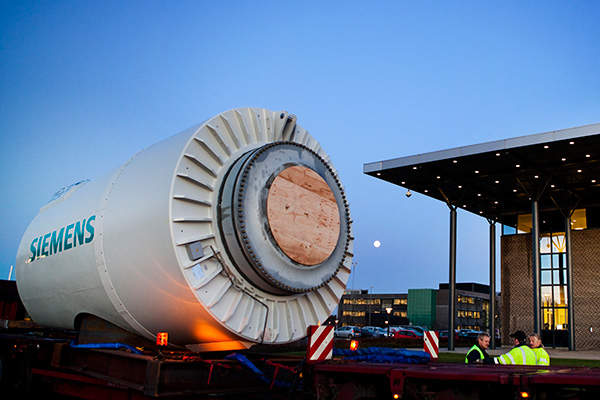
Siemens was selected to supply and install the direct drive turbines for the windfarm. It was the biggest ever direct-drive turbine contract Siemens has won in the UK. Siemens also services and maintains the windfarm during the operational phase, under a five-year service agreement.
ABB was responsible for providing grid connection and supplying the related transmission infrastructure. ABB designed and built two new substations and installed substation equipment, including the STATCOM units, PASS switchgear, transformers, as well as protection and control devices.
Express Reinforcements was contracted to supply steel reinforcement for the turbine bases and Prysmian Cables and Systems provided the cables to connect the two substations.