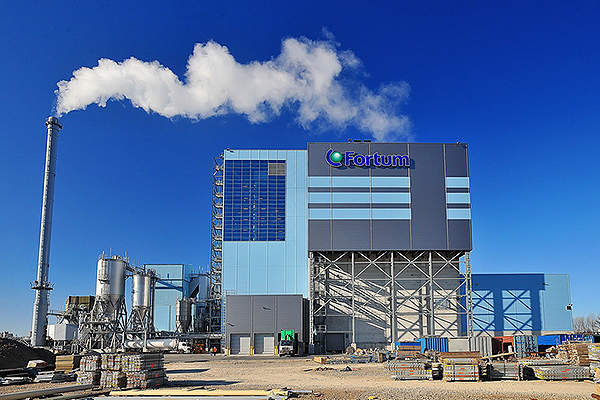
Fortum has developed a waste-to-energy conversion plant in the Baltic region of Klaipeda, Lithuania. The Klaipeda combined heat and power plant (CHPP) converts municipal and industrial waste, and biomass into heat and electricity. It is the first of four plants Fortum has planned to develop in the Baltic region.
The Klaipeda CHPP will generate 60MW of heat and 20MW of electricity per year. Klaipedos Energija will purchase the heat generated from the waste to energy plant.
Fortum is the owner and developer of the Klaipeda power plant. It holds 95% share in the project, while Klaipedos Energija holds the remaining 5%.
The Klaipeda heat and power plant involved an investment of €130m ($167m), which was financed by Nordic Investment Bank with €70m ($90m) loan. It was the largest foreign direct investment in Lithuania in 2012.
Klaipeda CHPP details
Fortum obtained the integrated pollution prevention and control permit for the Klaipeda CHPP in January 2013 after the plant was tested successfully. The plant officially commenced operations in May 2013.
The plant has the capacity to burn 230,000t of waste and biomass annually. The flue gas condensers at the plant are capable of recovering 15MW of heat in addition to generating heat and electricity.
Klaipeda CHPP is expected to produce 140GWh of electricity and 400GWh of heat per year, which is enough to meet approximately 40% of Klaipeda’s district heating demand.
Heat from the plant will be sold to Klaipedos Energija under third-party access and long-term competitive contract.
The Klaipeda CHPP is expected to cut 100,000t of carbon dioxide emissions per year. The district heat extraction equipment installed in the plant ensures high rate of energy utilisation. The concept of using sorted waste as fuel in combined heat and power generation is a good solution, especially in urban areas.
The plant is installed with Fisia Babcock boilers, which have a capacity to burn 230,000t of waste and biomass achieving a thermal output of 85MW.
The plant is also installed with safety manager emergency shutdown system, which will reduce the chances of accidents due to human error and asset damages in the plant.
Technology used at the combined heat and power plant
The Klaipeda CHPP uses Alstom’s NID flue gas cleaning equipment. The NID system is a semi-dry flue gas desulphurisation system that uses advanced technologies for multi-pollutant control and zero-waste water discharge.
The main concept behind semi-dry flue gas desulphurisation system is the reaction between sulphur dioxide and calcium hydroxide in humid conditions. The humidified mixture of hydrated lime and reaction product cools the inlet flue gas present in the NID system.
The flue gas is sent to the dust collector, where the gas particles are removed and processed back to the NID flue gas desulphurisation system.
The fabric filter of Klaipeda CHPP has the advantage of lower particulate emissions and can absorb additional gas in the dust cake. Water is added to the ash, received from the fabric filter, to increase the moisture content in the humidifier.
Suppliers involved with Fortum’s CHPP in Lithuania
The flue gas treatment and heat recovery system was supplied by Alstom. The flue gas treatment system included humidifiers, mixers, and waste treatment system.
Fisia Babcock was the EPC contractor for the boilers. It was responsible for the design, development and erection of the boilers, as well as commissioning and trial operation.
Honeywell provided the Experion Process Knowledge System (Human Machine Interface) and safety manager emergency shutdown for Klaipeda CHP plant.
Related content
Iberdrola Combined Cycle Power Plant, Lithuania
Iberdrola Ingeniería has taken up the construction of a combined cycle type power plant for government-owned Lietuvos Elektrine in Lithuania.
Siemens, GS E&C complete two combined-cycle power plant projects in Oman
Siemens Energy and its consortium partner GS Engineering & Construction (GS E&C) have completed and commissioned two combined-cycle power plant (CCPP) projects, Sohar 2 and Barka 3, in the Sultanate of Oman.