The lockdowns enforced to fight the COVID-19 pandemic have led to a decline in power consumption stalling some of the new projects temporarily.
Power Technology has conducted a poll to assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on power capacity addition.
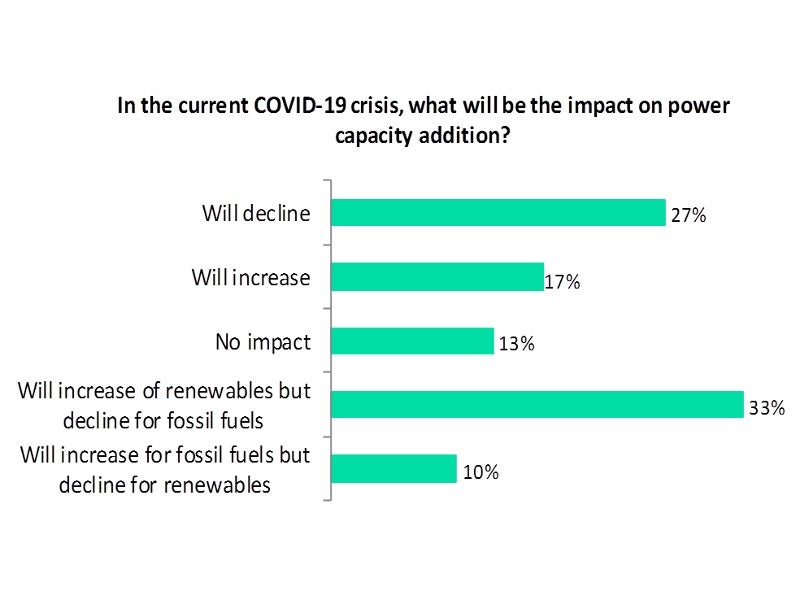
Analysis of the results shows that the pandemic will result in an increase in renewable power capacity addition and a simultaneous decrease in non-renewable capacity as voted by a majority one-third of the respondents.
Power capacity addition will decline in both the segments due to COVID-19, according to 27% of the respondents, while 17% respondents opined that power capacity addition will increase in both the segments amid the pandemic.
While 13% felt that COVID-19 would have no impact on power capacity addition, a minority 10% opined that non-renewable power capacity addition will increase and that of renewables will decrease.
The analysis is based on 429 responses received between 01 May and 01 June.
IEA’s view on the impact of COVID-19 on power capacity addition
The International Energy Agency (IEA) anticipates both renewable and non-renewable power capacity additions to suffer due to COVID-19.
Global energy consumption declined by 3.8% in the first three months of 2020 due to the lockdown restrictions imposed across the world, says IEA which adds that demand for coal-based electricity declined at the highest rate as user countries such as China and India.
Although the demand for renewables is projected to increase due to low operating costs and access to different power systems, IEA expects renewable power capacity to decline in 2020 due to supply chain disruptions and temporary construction halts.
A rebound is anticipated in 2021, however, according to IEA.
Wind and solar power installations to suffer a delay: GlobalData
Capacity declines apart, GlobalData foresees a delay in renewable projects due to supply chain disruptions.
Wind installations in India, for example, are expected to be delayed due to dependence on key equipment supplies from China.
Further, installed wind capacity in the UK is expected to decline by 0.24GW and solar photovoltaic capacity installation is projected to fall to 220MW, according to GlobalData.



