The Carmel River Reroute and San Clemente Dam (CRRDR) project is the largest dam removal project in California and the West Coast of US.
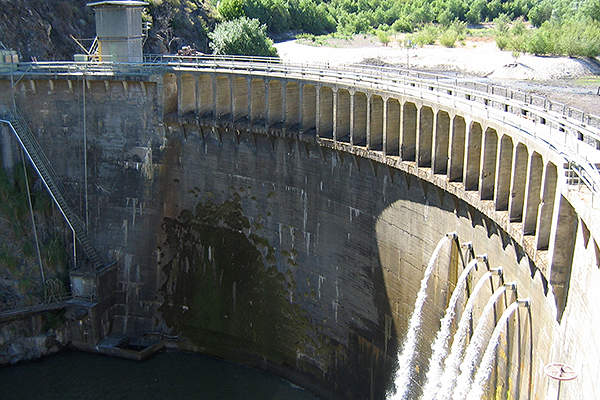
The project includes the removal of San Clemente Dam located on the Carmel River in Monterey County, and re-routing a 3,000ft section of the Carmel River into the San Clemente Creek River.
The project received the California Public Utilities Commission’s (CPUC) approval in June 2012. The Monterey County Planning Commission (MCPC) approved the project in May 2013.
California American Water (CAW) is the owner and operator of the dam, with URS Corp as its representative. CAW appointed Water Systems Consulting (WSC) as the project manager.
Construction works for the project began in 2013 and are expected to be completed by July 2015.
Financing the major dam removal project
The $84m project is being developed through a Public Private Partnership (PPP).
California American Water (CAW or Cal-Am) will provide $49m, while California State Coastal Conservancy (CSCC) and National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFC) will jointly provide an additional $35m from PPP sources.
The project is being supported by environmental organisations such as the Carmel River Watershed Conservancy and the Carmel River Steelhead Association. Nature Conservancy, a non-profit organisation, provided $1m for the project.
The project will also be funded by the California Department of Fish & Game, California Natural Resources Agency, California Wildlife Conservation Board and United States Fish & Wildlife Service.
Carmel River Reroute and San Clemente Dam history
The 106ft high San Clemente Dam is a concrete arch dam which was constructed in 1921. The dam initially had a 1,425acre-feet reservoir storage capacity. The storage capacity declined over the years owing to the huge amount of sediments totalling about 2.5 million cubic yards, almost covering about 90% of the entire water storage space.
The reduced storage capacity of the dam forced the authorities to remove it from the Monterey region’s water supply system in 2008.
The California Department of Water Resources (CDWR) Division of the Safety of Dams (DSOD) issued a safety order for the public, in the 1990s, that the dam will possibly fall in the event of an earthquake or probable maximum flood (PMF).
CDWR issued a Draft Environmental Impact Report (EIR) for the San Clemente Dam Seismic Safety Project (SCDSSP), which provided five solutions for the dam safety issue in 2006. The report included an idea of strengthening the dam, as well as removal including the current CRRDR project.
The dam strengthening idea was considered to be costly and could not provide the solution to the issue of removing the huge amount of sediment from the dam. The CRRDR project was considered as a better option.
The final EIR for the CRRDR project was received by CDWR in December 2007. The project received CDWR approval in February 2008. The CAW finally signed a deal with the federal government of the US to demolish the dam in 2010.
Details of the CRRDR project
The San Clemente dam is located at the meeting edge of the Carmel River and San Clemente Creek. The two rivers are further separated by a narrow ridge.
The Carmel River reservoir side stores majority of sediments. The CRRDR project will transfer the Carmel River sediments into a permanent sediment storage area, thus resolving the problem of excavating the huge amount of sediment from the dam. It will also reduce the project cost and will be environmentally beneficial.
The Carmel River will then be rerouted to the San Clemente Creek River, which will move the meeting point of the rivers upstream by half a mile. The up streaming of the meeting point will help in keeping the sediment area as it is. The sediment area is expected to be developed into a vegetated landscape.
The project will also involve cutting of a reroute channel to achieve the re-routing of rivers. The re-route channel will help divert the river flow from the sediment disposal area.
A new 400ft long diversion dike will be constructed using earth-fill material, in order to divert the river towards the new reroute channel. The dike will have a height of 45ft to 50ft. It will also have a seepage cutoff wall connected to the bedrock of the river.
The preliminary design of the dike is being developed by URS Corp. The dike will also feature a wedge-shaped slope that will be 700ft long and 70ft tall. The slope will be constructed upstream of the dam to store the sediments in the reservoir.
The sediments removed from the reservoir will be stored behind the stabilised sediment slope. The dam will be removed in stages once the construction of the dike and slope are completed. The partial removal of the dam is anticipated to begin in 2014 while the full removal is scheduled for mid 2015.
The half-mile reach on the San Clemente Creek reservoir side will be rebuilt to allow the combined passage of the river and the creek waters. Step pools will be created, by placing rocks across the channel’s bottom, to allow passage of fish through the reservoir. Fishes can rest on the rocks at the time of jumping into the river.
Development of new access road, relocation of fish and other wild life, and geotechnical investigations were completed during the first phase of construction, which also included the preparation of the 68-acre construction site and partial construction of the Carmel River diversion system.
The permanent routing of the Carmel River to an alternate course that bypasses the 2.5 million cubic yards of sediment is expected to be completed during the phase season of construction that began in May 2014.
Benefits of the dam removal and river reroute project
The project will provide public safety by averting dangers from a possible fall of the dam caused by an earthquake or lightning which is estimated to affect 1,500 homes downstream. It will also restore the natural sediments and reduce channel incision and beach erosion.
The project will also provide suitable habitation for endangered species of California, such as the steel cut fish and the red legged frog. It will support habitation under the river by transferring the sediment naturally downstream.
Contractors involved with the CRRDR project
The State Coastal Conservancy (SCC) manages the PPP scheme of the project and represents the project design, construction and permitting decisions to the funding partners. The SCC formed a Technical Review Team (TRT) of experts to analyse technical aspects of the project.
The main contractor for the project is Granite Construction, which received a $61m design-build contract from Cal-Am in May 2013. The contractual scope includes the removal of the dam and development of the new reroute channel.
CAW will transfer 928 acres of land after the dam’s removal to the US Department of Interior’s Bureau of Land Management (BLM). BLM is collaborating with the Monterey Peninsula Regional Parks District (MPRPD) to develop public access and recreation facilities on the land.
Related content
Calaveras Dam Replacement Project, United States of America
Calaveras Dam Replacement Project involves construction of a new earth and rock fill dam to replace the existing seismically unsafe dam and avoid flooding downstream.
Wolf Creek Dam Foundation Remediation Project, Kentucky, US
The US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) completed foundation remediation works for the Wolf Creek Dam in March 2013.