The ongoing energy crisis and the global goal to achieve net zero by 2050 have both encouraged the common effort to decarbonise the power sector and increase renewable share within the power mix.
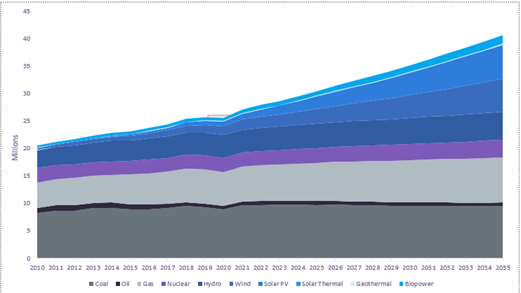
The latest report from GlobalData ‘Global Power Mix in Transition’ explores renewable’s opportunity to cover the increasing power demand forecasting a 47% share by 2035, comparatively with the 30% share it had by the end of 2022.
The power capacity needs to change to meet the demand of each region. Regions with a high population influence the compound annual growth of power as there is an increase in its usage. And even when most of the regions have started to increase their effort in pursuing renewable installations, some are still reliant on fossil fuel-based power, as in Africa and the Middle East.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind are commonly used renewable energy across different regions such as the Asia-Pacific and North America. Countries closer to the equator may use more solar PV energy as they are not impacted by the seasonal changes which impacts the daylight hours.
Although offshore wind is expected to increase its share of the mix from 8% to 20% by 2035, the majority of wind power comes from onshore. The power produced by the wind is expected to double from the year 2022 to 2035. This is due to the development of wind turbines in countries with a large mass of area such as Brazil, China, Australia, the US, and the UK.
South and Central America are highly dependent on hydropower as water resources are abundant in the regions. Energy supply is quickly transitioning into renewable energy-based, due to increasing investments and advancements in technological developments.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalDataReports
Power Mix in Transition by Region, Technology and Disruptive Themes, 2023-2035
These innovations are extremely important in countries such as Colombia, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Brazil as it is predicted to be fully powered by renewables by 2035. Other renewable energies used are solar PV and wind which have had exponential growth since 2022, resulting in tripling their generation levels by 2035.
On the other side, Europe is currently going through an energy crisis, which has pushed it to switch energy suppliers to cover its energy demand. This would mean an opportunity for the region to adapt and become energy-sufficient and focus on the development of clean and reliable energy sources.
Countries such as Austria, France, the UK, Italy, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Germany have started phasing out coal, supporting GlobalData’s renewable energy forecast to hit 60% by 2035.
But even when renewable is peaking up and there is a common effort to develop a cleaner energy supply, countries such as France and Germany have as well reactivated their nuclear plants and created new gas projects in order to cover their demand.
Even though thermal power dependency is starting to decrease due to phasing-out coal policies and a reduction in oil-fired power generation, transitioning out from fossil fuels is more challenging in regions where they are the economic main support, as in the Middle East and Africa.
And even when they have been actively increasing their renewable capacity installations, currently making 22% of their power mix, fossil-based power keeps being cheaper and the most competitive source of energy.
Currently, clean market technologies will continue to increase generation to cover the global power demand, in particular, wind and solar power will have an impact in all regions increasing their share dramatically. These technologies’ costs have started to decrease dramatically given technological advancement and increasing investments, hence becoming more competitive.